Landscape CRM: A Comprehensive Guide
Landscape CRM isn’t your grandpappy’s CRM. Forget stuffy spreadsheets and clunky interfaces; this is about a holistic approach to customer relationship management, tailored to understand the unique needs of diverse businesses. We’ll delve into its core features, benefits, and the exciting future of this innovative system, exploring how it transforms sales, boosts productivity, and ultimately, helps businesses thrive.
This guide will cover everything from defining Landscape CRM and differentiating it from traditional systems to outlining a practical implementation plan and addressing potential challenges. We’ll explore data visualization techniques, analyze successful case studies, and even peek into the future trends shaping this dynamic field. Get ready to rethink how you manage customer relationships.
Defining Landscape CRM
Landscape CRM isn’t your grandpappy’s customer relationship management system. While traditional CRMs focus on managing individual customer interactions, Landscape CRM takes a broader, more holistic approach, focusing on managing relationships across entire ecosystems. Think less about individual customer profiles and more about the complex web of interactions between businesses, suppliers, partners, and even competitors within a specific industry or geographical area.
This shift in perspective allows for a deeper understanding of market dynamics and competitive landscapes. Instead of siloed customer data, Landscape CRM provides a comprehensive view of the entire industry ecosystem, enabling businesses to make more strategic and informed decisions.
Key Features and Functionalities of Landscape CRM
Landscape CRM distinguishes itself through its ability to integrate and analyze data from diverse sources, going beyond traditional customer data. This includes market research data, competitor analysis, regulatory information, and even environmental factors impacting the industry. This comprehensive data integration allows for powerful analytical capabilities not found in standard CRMs.
- Ecosystem Mapping: Visual representation of the relationships and interactions within a specific industry or geographic area, allowing for identification of key players and influential relationships.
- Competitive Intelligence: Advanced tools for monitoring competitor activities, including market share, pricing strategies, and new product launches. This often includes sentiment analysis from online sources and news feeds.
- Supply Chain Visibility: Tracking and managing relationships with suppliers, distributors, and other partners throughout the supply chain, identifying potential bottlenecks and risks.
- Regulatory Compliance Monitoring: Staying up-to-date on relevant regulations and ensuring compliance through automated alerts and reporting features.
- Predictive Analytics: Using historical data and advanced algorithms to forecast market trends, predict customer behavior, and optimize business strategies. For example, predicting potential supply chain disruptions based on weather patterns or geopolitical events.
Typical Use Cases and Industries
Landscape CRM finds its most effective applications in industries with complex ecosystems and a high degree of interdependence between businesses. The ability to understand and manage these complex relationships provides a significant competitive advantage.
- Real Estate: Understanding the relationships between developers, contractors, buyers, and local governments to optimize project planning and risk management.
- Agriculture: Managing relationships with farmers, distributors, retailers, and consumers, while considering factors like weather patterns and crop yields.
- Pharmaceuticals: Analyzing the complex relationships between pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, regulatory bodies, and healthcare providers to accelerate drug development and market entry.
- Financial Services: Understanding the intricate network of financial institutions, regulatory bodies, and investors to manage risk and optimize investment strategies. For example, a bank could use it to model the impact of a competitor’s new product launch on their own customer base.
Benefits and Advantages of Landscape CRM
Let’s face it, a Landscape CRM isn’t just another CRM; it’s a game-changer. It offers a holistic view of your customer interactions, moving beyond simple contact management to encompass the entire ecosystem influencing your business. This integrated approach unlocks significant advantages over traditional CRM strategies, leading to increased efficiency and profitability.
This section details the key benefits and advantages of adopting a Landscape CRM approach, focusing on its impact on sales productivity and customer relationship management, and highlighting the key performance indicators you can track and improve.
Improved Sales Productivity
A Landscape CRM significantly boosts sales productivity by providing sales teams with a complete, 360-degree view of each prospect and client. This comprehensive understanding eliminates information silos, reducing time spent searching for data and enabling faster, more informed decision-making. For instance, if a sales rep knows a client’s past purchasing history, project timelines, and communication preferences, they can tailor their approach for maximum impact, increasing conversion rates and shortening the sales cycle. This integrated data flow streamlines the sales process, allowing reps to focus on building relationships and closing deals rather than administrative tasks.
Enhanced Customer Relationship Management
Landscape CRM fosters stronger customer relationships by providing a centralized platform for managing all customer interactions. This allows businesses to understand customer needs and preferences more deeply, leading to personalized experiences and improved customer satisfaction. Imagine having all communication channels – emails, phone calls, social media interactions – neatly organized and readily accessible. This facilitates proactive customer service, enabling rapid response to queries and issues, and preventing potential problems before they escalate. The result? Increased customer loyalty and advocacy.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Several key performance indicators (KPIs) can be tracked and improved using a Landscape CRM. These metrics provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of your CRM strategy and allow for data-driven adjustments. For example, you can track metrics such as sales conversion rates, customer acquisition cost, customer lifetime value, and customer satisfaction scores. By monitoring these KPIs, businesses can identify areas for improvement and optimize their processes for maximum efficiency and profitability. A significant increase in customer lifetime value, for example, could indicate a successful strategy of personalized engagement and proactive service, directly attributable to the comprehensive data management capabilities of the Landscape CRM.
Implementation and Integration of Landscape CRM
Successfully implementing a Landscape CRM involves careful planning and execution. A phased approach minimizes disruption and maximizes the return on investment. This section details a step-by-step plan and explores integration strategies with existing systems.
Step-by-Step Implementation Plan for a Landscape CRM System
A successful implementation follows a structured approach. This plan outlines key phases, ensuring a smooth transition and optimal system utilization.
- Needs Assessment and Goal Definition: Clearly define your business objectives and how a CRM will help achieve them. Identify key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure success.
- Software Selection and Vendor Evaluation: Research and compare different CRM options, considering factors like cost, features, scalability, and integration capabilities. Request demos and thoroughly evaluate each system against your needs.
- Data Migration and Cleansing: Transfer existing customer and project data into the new CRM system. This often requires data cleansing to ensure accuracy and consistency. Expect this to be a time-consuming process.
- System Configuration and Customization: Configure the CRM to match your specific business processes and workflows. This might involve customizing fields, reports, and dashboards.
- User Training and Onboarding: Provide comprehensive training to your team on how to effectively use the CRM system. Hands-on training and ongoing support are crucial for adoption.
- Go-Live and Initial Monitoring: Launch the CRM system and closely monitor its performance. Address any issues promptly and make necessary adjustments.
- Ongoing Optimization and Improvement: Regularly review and refine your CRM processes based on user feedback and performance data. Continuous improvement is key to maximizing the system’s value.
Comparison of Landscape CRM Software Options
Choosing the right software is crucial. This table compares three hypothetical examples, focusing on key factors. Remember that actual pricing and features vary depending on the provider and specific package.
| Software Name | Cost (USD/month, per user) | Key Features | Scalability |
|---|---|---|---|
| GreenThumb CRM | $50 – $150 | Job scheduling, client management, inventory tracking, basic reporting | Small to medium-sized businesses |
| LandscaperPro | $75 – $250 | Advanced job scheduling, client portal, integrated payments, custom reporting, mobile app | Medium to large-sized businesses |
| BloomTech CRM | $100 – $350 | All features of LandscaperPro, plus advanced analytics, API integrations, and multi-location support | Large businesses with complex needs |
Integrating Landscape CRM with Existing Business Systems and Data Sources
Seamless integration is key to maximizing efficiency. This involves connecting the CRM with other systems like accounting software, scheduling tools, and email marketing platforms.
Integration methods vary depending on the software involved. Common approaches include:
- API Integrations: Many CRM systems offer Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that allow for direct data exchange with other software. This offers the most robust and flexible integration.
- Data Import/Export: Simpler integrations can be achieved by importing and exporting data files (like CSV or XML) between systems. This is less efficient but may suffice for less complex needs.
- Third-Party Integration Tools: Several tools specialize in connecting different software applications. These tools can simplify the integration process, especially for systems without native API support.
Successful integration requires careful planning and coordination. Consider factors like data security, data mapping, and potential data conflicts during the integration process. Thorough testing is essential to ensure data integrity and system stability after the integration.
Challenges and Considerations of Landscape CRM
Implementing a Landscape CRM, while offering significant benefits, presents several challenges that need careful consideration. Successfully navigating these hurdles requires proactive planning, robust data management strategies, and a commitment to ongoing training and adaptation. Ignoring these challenges can lead to system failure, data loss, and ultimately, a poor return on investment.
Choosing the right Landscape CRM system is only the first step. The true test lies in its successful implementation and ongoing management. Several key areas require attention to ensure a smooth transition and maximize the system’s potential.
Data Migration and Integration
Migrating existing client and project data into a new CRM system can be a complex and time-consuming process. Data inconsistencies, outdated information, and the need to transform data into a compatible format all contribute to the difficulty. For example, a company might have client information spread across spreadsheets, email accounts, and handwritten notes. Consolidating this disparate data into a unified system requires careful planning and potentially the use of data cleansing and migration tools. Effective data mapping is crucial to ensure that data fields are correctly aligned between the old and new systems. Poor data migration can lead to inaccurate reporting and compromised decision-making.
User Adoption and Training
Successful CRM implementation hinges on user adoption. If employees don’t understand how to use the system effectively, it will remain underutilized and fail to deliver its promised benefits. Comprehensive training programs are essential, covering everything from basic navigation to advanced features. Ongoing support and readily available resources are equally crucial to address user queries and resolve technical issues. Resistance to change is a common obstacle, and addressing employees’ concerns and providing adequate support is key to overcoming this. For instance, a phased rollout approach, starting with a pilot group, can help identify and resolve training issues before a full-scale deployment.
Data Security and Privacy
Landscape CRMs often store sensitive client data, including personal information, financial details, and project specifics. Robust security measures are therefore paramount. This includes implementing access controls, encryption, regular data backups, and compliance with relevant data privacy regulations like GDPR or CCPA. Data breaches can have serious consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, and legal penalties. A comprehensive security policy, regular security audits, and employee training on data security best practices are vital components of a secure CRM environment. For example, implementing multi-factor authentication and regularly updating software can significantly enhance security.
System Maintenance and Updates
A CRM system is not a “set it and forget it” solution. Ongoing maintenance, including regular software updates, data backups, and performance monitoring, is essential to ensure its continued functionality and security. Failure to perform regular maintenance can lead to system instability, data corruption, and security vulnerabilities. Budgeting for ongoing maintenance costs and assigning dedicated personnel to manage these tasks is crucial for long-term success. Proactive maintenance minimizes downtime and prevents major issues from arising.
Cost and Return on Investment
The initial investment in a Landscape CRM system can be significant, encompassing software licensing, implementation costs, training, and ongoing maintenance. Accurately assessing the return on investment (ROI) requires careful planning and a clear understanding of the system’s potential benefits. Defining key performance indicators (KPIs) and tracking them over time is crucial to measuring the success of the implementation. For example, improvements in client retention rates, increased sales efficiency, or reduced administrative overhead can all contribute to a positive ROI. Failure to properly track and analyze KPIs can make it difficult to demonstrate the value of the CRM system.
Landscape CRM and Data Visualization
Effective data visualization is crucial for leveraging the insights gleaned from a Landscape CRM system. By transforming raw data into easily digestible visuals, businesses can gain a clearer understanding of their performance, identify areas needing improvement, and make data-driven decisions to boost profitability and efficiency. This section explores how to effectively visualize key data insights and present them to various stakeholders.
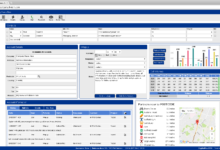
Dashboard Examples for Landscape Performance Tracking
Dashboards provide a high-level overview of key performance indicators (KPIs). A well-designed dashboard allows quick identification of trends and potential problems. For example, a Landscape CRM dashboard might display real-time metrics such as the number of active clients, the total revenue generated, the average job completion time, and the number of new leads acquired. Another section could show a geographical distribution of clients, highlighting areas of high concentration or potential for expansion. A final section might track key customer satisfaction metrics, such as average customer rating and the number of positive reviews. These visual representations help managers quickly assess the overall health of the business and identify areas requiring attention.
Client Acquisition Cost and Revenue Analysis Report
A detailed report focusing on client acquisition cost (CAC) and revenue generation provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of marketing and sales strategies. This report would compare the cost of acquiring new clients against the revenue generated by those clients, allowing for a calculation of return on investment (ROI). It can also identify which marketing channels are most effective in generating high-value clients.
| Month | Marketing Spend | New Clients Acquired | Revenue Generated | CAC | ROI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | $5000 | 10 | $20000 | $500 | 300% |
| February | $3000 | 8 | $15000 | $375 | 400% |
| March | $6000 | 12 | $25000 | $500 | 316% |
This table provides a clear and concise view of the financial performance of client acquisition efforts across different months. Managers can use this data to optimize their marketing strategies and improve the ROI.
Data Visualization Techniques for Different Stakeholders
Choosing the right visualization technique depends heavily on the audience and the message being conveyed. For example, a simple bar chart might suffice for presenting high-level performance metrics to senior management, while a more detailed geographical heatmap could be used to illustrate client distribution to regional sales teams. Interactive dashboards, allowing for drill-down analysis, are particularly effective for empowering individual team members to explore data at a granular level. For presentations to investors, concise charts and graphs highlighting key financial metrics would be most appropriate. The use of clear, concise labels and titles is crucial for all visualizations to ensure accurate and easy understanding regardless of the audience’s technical expertise.
Future Trends in Landscape CRM
The landscape of CRM, even within the niche of landscape businesses, is constantly evolving. Technological advancements and changing customer expectations are driving significant shifts in how these systems are designed, implemented, and utilized. We’ll explore key trends that will define the future of Landscape CRM in the coming years.
The integration of increasingly sophisticated technologies will fundamentally alter the way landscape companies manage their operations and customer relationships. This evolution will lead to more efficient workflows, enhanced customer experiences, and ultimately, improved profitability.
AI and Machine Learning in Predictive Maintenance
AI and machine learning are poised to revolutionize predictive maintenance within landscape CRMs. By analyzing historical equipment data (e.g., operating hours, service records, sensor readings), AI algorithms can predict potential equipment failures before they occur. This allows for proactive maintenance scheduling, minimizing downtime and reducing repair costs. For instance, a system could analyze the performance data of a particular mower and predict a potential engine failure within the next two weeks, prompting a scheduled maintenance check to avoid a costly breakdown mid-project. This predictive capability extends beyond equipment to encompass labor allocation, predicting peak workload periods and allowing for optimized staffing.
Increased Use of IoT and Sensor Data
The Internet of Things (IoT) and the associated influx of sensor data will significantly enhance the capabilities of Landscape CRMs. Integrating smart irrigation systems, soil moisture sensors, and GPS-tracked equipment provides real-time insights into operational efficiency and resource utilization. A CRM could integrate data from a smart irrigation system, automatically adjusting watering schedules based on real-time soil moisture levels, saving water and improving plant health. This data, coupled with GPS tracking of equipment, could further optimize routes, reducing fuel consumption and travel time.
Enhanced Customer Relationship Management through Personalization
Future Landscape CRMs will place a greater emphasis on personalized customer interactions. By leveraging data analytics and AI, these systems can segment customer bases and tailor communication strategies to individual preferences. This could involve automated email campaigns promoting services relevant to a specific customer’s property type or offering personalized discounts based on past spending habits. The CRM could, for example, automatically generate a targeted email to a customer who hasn’t booked a lawn mowing service in the past two months, offering a special discounted rate. This targeted approach strengthens customer relationships and fosters loyalty.
Improved Mobile Accessibility and Integration
Mobile accessibility will continue to be a critical factor in the success of Landscape CRMs. Future systems will offer seamless integration with mobile devices, allowing field technicians to access and update customer information, schedule appointments, and generate invoices in real-time. This streamlined workflow reduces administrative overhead and improves overall operational efficiency. A field technician, for instance, could update a customer’s service record directly from their mobile device after completing a job, ensuring accurate and up-to-date information is readily available.
Blockchain Technology for Secure Data Management
While still in its early stages of adoption in the CRM space, blockchain technology offers the potential for enhanced data security and transparency within Landscape CRMs. By using blockchain, companies can securely store and manage sensitive customer data and operational records, ensuring data integrity and minimizing the risk of fraud or data breaches. This enhanced security builds trust with customers and protects valuable business information. For example, a company could use blockchain to securely store customer payment information, reducing the risk of data breaches and ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations.
Case Studies of Successful Landscape CRM Implementations
Real-world examples demonstrate the tangible benefits of implementing a Landscape CRM. Analyzing successful deployments reveals best practices and highlights the diverse ways this technology can improve business operations across different landscape companies. This section presents detailed case studies illustrating these successes and the lessons learned.
GreenThumb Landscaping: Streamlining Operations and Improving Client Retention
GreenThumb Landscaping, a mid-sized company serving a suburban area, faced challenges with scheduling, client communication, and project management. Their previous system relied on spreadsheets and email, leading to inefficiencies and missed opportunities. Implementing a Landscape CRM system addressed these issues.
- Implementation Process: GreenThumb chose a cloud-based CRM, opting for ease of access and scalability. The implementation involved thorough data migration from their existing spreadsheets, employee training, and a phased rollout to minimize disruption.
- Key Results: After implementation, GreenThumb experienced a 15% increase in client retention, a 20% reduction in scheduling conflicts, and a 10% improvement in project completion times. The CRM’s automated communication features also freed up staff time, allowing them to focus on client interactions and project execution.
- Lessons Learned: Thorough employee training was crucial for successful adoption. GreenThumb also emphasized the importance of ongoing data maintenance and system optimization to maximize the CRM’s benefits. Regular review of reporting dashboards enabled proactive adjustments to their business strategies.
Evergreen Gardens: Enhancing Sales and Marketing Effectiveness
Evergreen Gardens, a larger landscape company with multiple branches, utilized a Landscape CRM to improve sales and marketing efforts, focusing on targeted campaigns and lead nurturing.
- Implementation Process: Evergreen Gardens integrated their CRM with their marketing automation platform, enabling automated email campaigns, targeted advertising, and personalized client communications. This required a more complex implementation process involving API integrations and data mapping.
- Key Results: The integrated CRM system resulted in a 25% increase in sales leads, a 10% conversion rate improvement, and a significant increase in customer lifetime value. The targeted marketing campaigns proved highly effective, leading to a better return on investment for their marketing efforts.
- Lessons Learned: The successful integration of the CRM with other business systems was critical. Evergreen Gardens also learned the importance of regularly analyzing marketing campaign data to refine their strategies and maximize their impact. They also emphasized the need for ongoing data cleansing to ensure the accuracy of their marketing lists.
Comparison of Case Studies
GreenThumb and Evergreen Gardens demonstrate the versatility of Landscape CRMs. GreenThumb focused on operational efficiency and client retention, while Evergreen Gardens prioritized sales and marketing. Both companies achieved significant improvements, but their approaches and outcomes differed based on their specific needs and goals. The choice of CRM system and implementation strategy should align with the company’s unique business objectives and existing infrastructure. The key takeaway is that a well-implemented Landscape CRM can significantly enhance various aspects of a landscaping business, regardless of its size or focus.
Final Review
Ultimately, embracing Landscape CRM is about more than just software; it’s a strategic shift towards a more insightful and responsive approach to customer engagement. By understanding its capabilities, addressing potential hurdles, and leveraging data visualization effectively, businesses can unlock significant improvements in sales productivity, customer satisfaction, and overall growth. The future of CRM is here, and it’s a landscape worth exploring.